A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE ON JOINT EFFUSIONS
A Comprehensive Guide on Joint Effusions

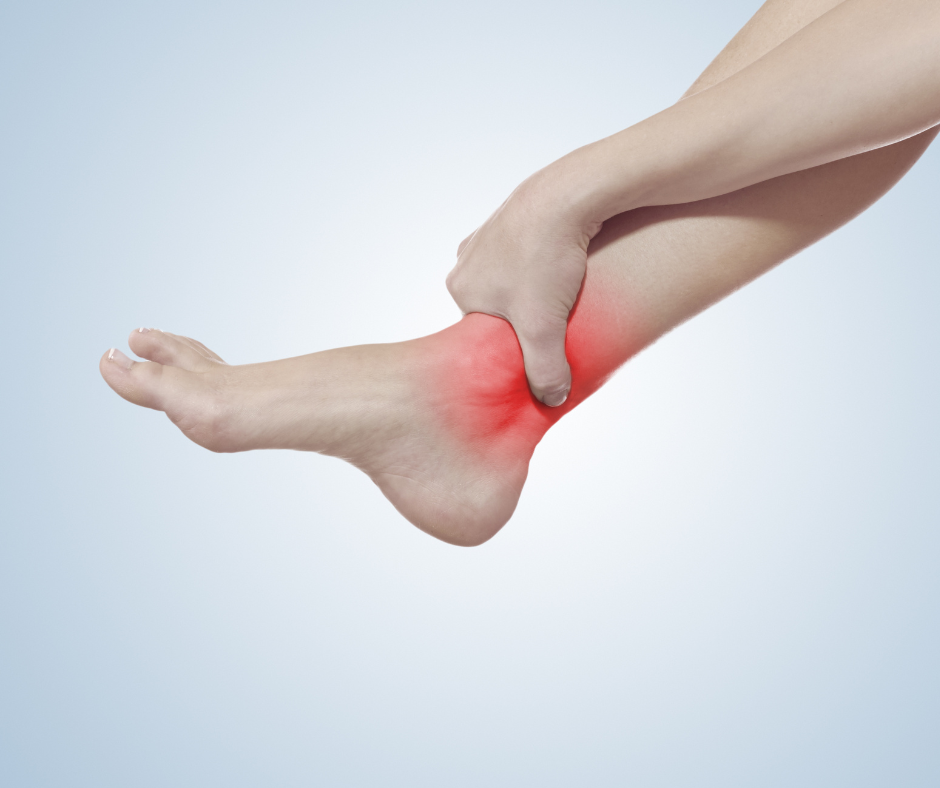
Joint effusion, commonly referred to as “water on the knee” or swelling in other joints, is a condition that occurs when excess fluid accumulates in or around a joint. While this phenomenon can affect any joint, it is most often seen in larger joints such as the knee, elbow, or shoulder. Beyond its visible swelling, joint effusion can indicate underlying health issues ranging from trauma to systemic diseases.
Let’s explore the details of joint effusion, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatment options.
What Is Joint Effusion?
At its core, joint effusion is the abnormal collection of fluid within a joint capsule. The synovial membrane, which lines joints, produces a lubricating fluid called synovial fluid. In normal amounts, this fluid reduces friction and aids joint movement. However, inflammation, injury, or certain medical conditions can cause an overproduction of this fluid or leakage of other bodily fluids into the joint, leading to swelling.
The fluid composition varies depending on the underlying cause. For instance, it may contain blood in cases of trauma or infection-related pathogens like bacteria.
Causes of Joint Effusion
Joint effusion arises from a myriad of triggers. In some cases, it is a direct result of an injury, while in others, it stems from chronic conditions or infections. Common causes include:
Injury and Trauma
Acute injuries, such as ligament tears, meniscus damage, or fractures, often lead to joint effusion. The body’s inflammatory response to these injuries results in swelling as blood and other fluids accumulate around the joint.
Arthritis
Various forms of arthritis are leading contributors to joint effusion. Osteoarthritis, caused by the gradual wear and tear of cartilage, triggers swelling in response to joint degeneration. Conversely, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease, prompts inflammation that leads to significant joint swelling.
Infections
Septic arthritis occurs when an infection infiltrates the joint space, leading to rapid swelling, pain, and fever. To prevent severe complications, this condition requires immediate medical attention.
Systemic Conditions
Diseases such as lupus, Lyme disease, or psoriatic arthritis can contribute to joint effusion. These conditions often affect multiple joints simultaneously and are accompanied by systemic symptoms.
Identifying Symptoms
Joint effusion manifests with a range of symptoms, varying in severity based on its underlying cause. The most noticeable sign is swelling, which may make the joint appear enlarged compared to its counterpart. Other symptoms include:
- Pain and Tenderness: Increased fluid within the joint capsule exerts pressure on surrounding tissues, resulting in discomfort.
- Limited Range of Motion: Swelling and inflammation can impede the joint's normal movement.
- Warmth and Redness: In cases involving infection or acute inflammation, the skin over the joint may feel warm to the touch or appear reddened.
- Instability: Depending on the joint involved, effusion can lead to feelings of instability or difficulty bearing weight.
Diagnosing Joint Effusion
A thorough medical evaluation is needed to pinpoint the cause of joint effusion. The diagnostic process often begins with a detailed history and physical examination. Physicians may inquire about recent injuries, ongoing illnesses, or family history of joint-related conditions.
Several diagnostic tools are employed to confirm the presence of effusion and its underlying cause:
Imaging Studies
X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasounds are commonly used to visualize the extent of joint swelling, detect fractures, or assess for degenerative changes like arthritis.
Joint Aspiration
Also known as arthrocentesis, this procedure involves extracting fluid from the swollen joint using a needle. The fluid is then analyzed to identify signs of infection, crystals, or blood.
Laboratory Tests
Blood tests help detect systemic markers of inflammation (e.g., ESR and CRP) or specific conditions like gout or autoimmune diseases.
Treatment Options
Treatment for joint effusion focuses on addressing both the swelling and its root cause. Depending on the diagnosis, options range from conservative management to more invasive interventions.
Conservative Approaches
For mild cases, especially those related to injury or overuse, rest and self-care can be sufficient. Techniques include:
- R.I.C.E Method: Rest, ice application, compression, and elevation are fundamental for reducing swelling and pain.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Medical Interventions
More severe cases often require medical attention. Common treatments include:
- Corticosteroid Injections: For conditions like arthritis, injecting steroids directly into the joint can reduce inflammation and provide significant pain relief.
- Antibiotics: In cases of septic arthritis, intravenous antibiotics are crucial to eliminate the infection and prevent joint destruction.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Post-treatment rehabilitation is essential for restoring joint function and preventing future effusion episodes. A tailored physical therapy program can strengthen muscles around the joint and improve mobility.
Surgical Interventions
When conservative and medical treatments fail, surgical options may be necessary. These can range from arthroscopic procedures to repair joint damage to joint replacement surgeries in severe arthritis cases.
Managing Joint Effusion
While treatment can effectively address acute joint effusion, prevention and management of recurrent episodes are equally important. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in low-impact exercises, can significantly reduce stress on joints and minimize the risk of future effusion.
Individuals with chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout should work closely with their healthcare providers to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Regular check-ups, adherence to prescribed medications, and lifestyle adjustments play pivotal roles in long-term joint health.
When to Seek Immediate Help
Although joint effusion is often manageable, certain symptoms signal a need for urgent care. These include sudden and severe swelling, intense pain, fever, or an inability to move the joint. These signs may indicate septic arthritis or a serious injury requiring immediate medical intervention.
At
AZ Ortho, our dedicated team specializes in diagnosing and treating joint effusions, offering personalized care to get you back to living pain-free.
Contact us today and take the first step toward lasting mobility and comfort!